AI in National Defense: Introduction of AI Pilot
Alpha Dogfight
5:0 sweep in simulated flight
International regulation on AI technology
The US is reportedly set to begin test flights on uncrewed combat aircraft powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
According to news outlets, including The Register, the US Air Force has delivered three F-16 Falcon fighter jets to Eglin Air Force Base for the Venom Project test. The F-16s are equipped with an autonomous flight system that is currently being developed and are soon expected to commence test flights.
A pilot will be on board to test the interaction between the AI model and the pilot and its efficiency in autonomous flight systems and other functions. The Venom Project, undertaken by the US, is known as the AI model development project to employ fighting jets without human intervention.

The US anticipates this research will be crucial in exploring new approaches and technologies for future air combat, such as Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA).
AI technology is the initiative of the military power in each country globally, with several countries striving to incorporate it into their military technologies. Furthermore, the real usage of AI technology in the Ukraine and Russia wars has brought AI issues to the table.
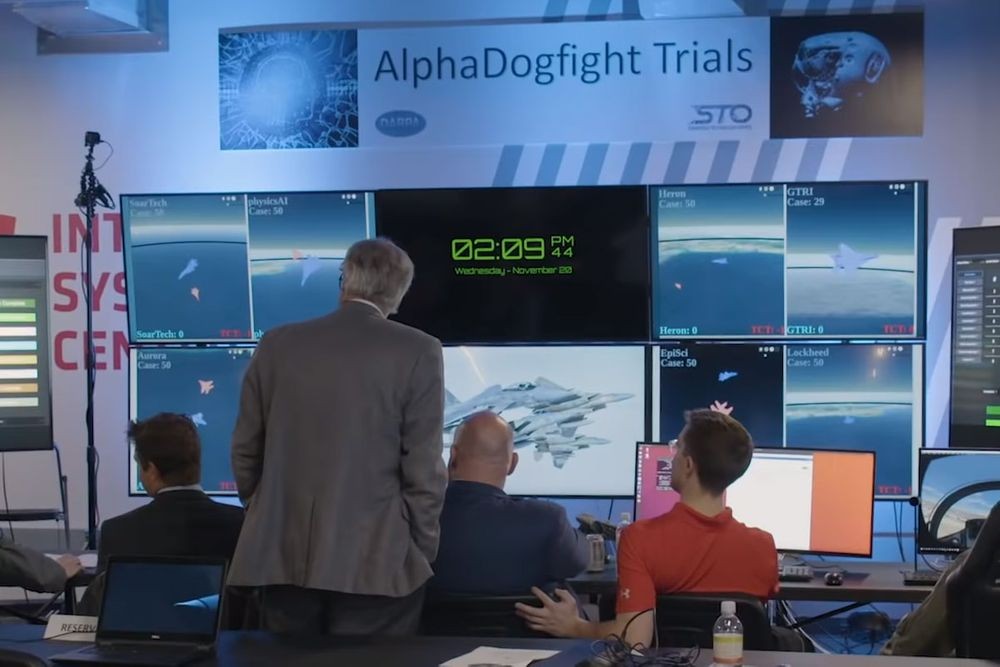
The potential for military application of AI was highlighted during the live broadcast of the Alpha Dogfight Challenge finals in 2020.
The Alpha Dogfight Challenge refers to the Maneuver Warfare AI algorithm developed by training fighter jets on close air combat data, similar to the machine-learning program AlphaGo absorbing mass data of Go game records.

The contest was a simulated flight duel between an AI pilot and a human pilot, conducted in a hackathon-style by the US Air Force to select the best maneuvering AI algorithm. Despite the human pilot being an active operator of the F-16, the AI pilot, developed by AI venture firm Heron Systems, won with a sweeping 5:0 victory.
The Alpha Dogfight continuously evolves, applying autonomous technology to develop weapons and change combat methods. It is projected that fighter jets equipped with AI pilots will be deployed in actual combat, performing auxiliary tasks to human pilots and eventually leading to a fully unmanned combat aircraft squadron.
A representative example is the Loyal Wingman, the development project for autonomous AI drones. The Loyal Wingman project conducts enemy INTEL surveillance and strikes by networking autonomous AI drones with human-crewed fighter jets to maximize survivability and combat effectiveness. Experts predict this technology will be completed and introduced to the battlefield by 2040.

Ultimately, only autonomous drones and unmanned combat aircraft squadrons are anticipated to engage in machine-to-machine combat.
AI technology is not limited to fighter jets and aerial drones. The US Navy reportedly created a ghost fleet with the uncrewed autonomous ship, Sea Hunter. This ghost fleet will form a vast manned-unmanned complex system, combined with AI drones and uncrewed surface vessels and submarines, establishing a C4I (command, control, communications, computers, and intelligence) system with far-distant carrier battle groups to assist precision strike missions.
Uncrewed vehicles and robots have evolved from simple initial remote operation and automatic modes to AI-based autonomous weapons on the ground. The US Army’s autonomous robot uncrewed combat vehicle has been confirmed to perform up to expectations. Enable to navigate based on its exploration data, selecting optimized maneuver routes, and completing tasks.
As AI technology advances, it is used to conduct tasks and explore the possibility of taking the assistant role of the commander’s decision-making and judgment on the battlefield. For instance, the US Army is reportedly close to completing the AI combat staff development required in urban warfare for small units.

This will provide real-time integrated analysis exceeding human capabilities of various sensor information implemented by friendly forces and INTEL necessary to conduct combat, such as C2 (Command and Control), MNVR (Maneuver), Fires, Protection, and SUS (Sustain and Support), to commanders and combatants to assist immediate commander’s decisions.
Since AI weapons have already been deployed in the Ukraine and Russia War, the broad military application of AI technology is a foregone conclusion. South Korea also appears eager to apply AI technology within the military. ROKA (Republic of Korean Army) anticipates a sharp decline in the workforce due to low birth rates and aging, deriving increased deployment of unmanned systems by designating a demonstration unit and establishing the ‘ARMY TIGER’ system.
Various combat experiments are also being conducted to enhance collaboration capabilities with operated systems. ROKAF (Republic of Korean Air Force) is also promoting the Smart Flight project, which combines AI with flight missions and overall air base operations, further developing the AI-based manned-unmanned combat flight system called ‘Kill-Web’ in preparation for future wars. ROKN (Republic of Korean Navy) is also pushing to construct AI-based intelligent ships and intelligent fleets.

Meanwhile, the international community has issued regulations on the military introduction of AI technology, as AI technology is expected to be applied across the military. Last year, 46 countries, including the US and South Korea, adopted a political declaration to use AI technology responsibly in the military.
This political declaration includes provisions for the responsible use of AI technology in military applications. It outlines ten specific measures to guide the responsible development and use of ‘autonomy,’ which refers to AI’s independent decision-making and operating system disregarding human intervention.
On the 21st, the UN passed a resolution to maintain safe and reliable AI systems for sustainable development worldwide. This resolution emphasizes the need for safe and trustworthy security standards for AI systems. It proposes sharing benefits through sustainable development methods so that AI’s benefits can reach all countries, especially developing countries.













Most Commented